Understanding the Differences: MSP vs MSSP
In today’s digital landscape, it’s crucial to understand the differences and benefits of Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs). These are two key players that businesses leverage to ensure their IT systems run smoothly and securely. But what sets them apart?
I. Managed Service Providers (MSP)
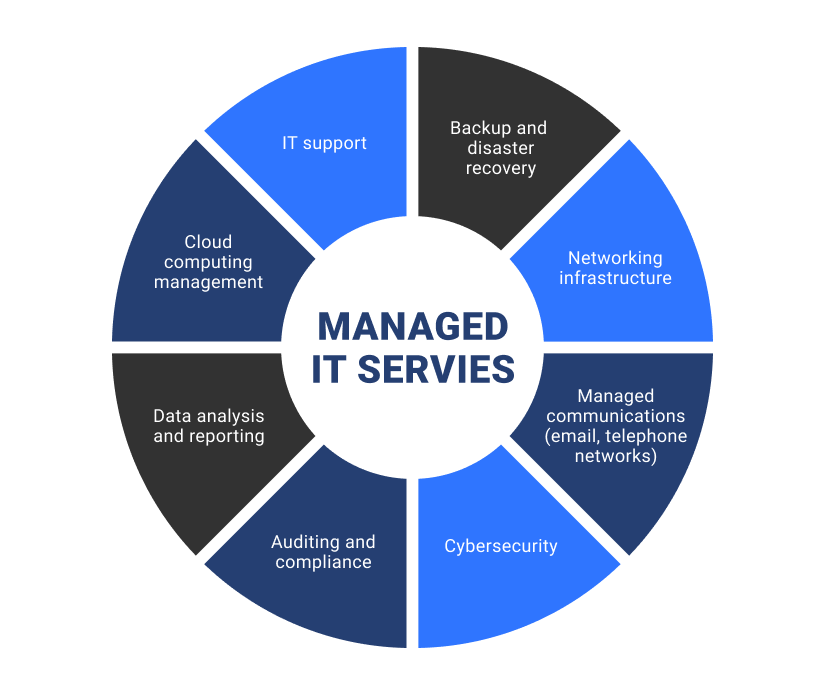
An MSP offers a range of IT services. They manage a company’s IT infrastructure, ensuring systems remain operational and efficient.
Roles and Responsibilities of MSP
Here’s a closer look at what an MSP does:
- Network Maintenance: They monitor and maintain your network to ensure it remains operational and efficient.
- Server Management: They manage your servers to ensure they remain up and running at optimal performance.
- Application Support: They offer support for all IT-related applications.
- Infrastructure Management: They manage your entire IT infrastructure, including hardware and software systems.
Proactive Approach to IT
MSPs don’t just fix problems; they proactively look for ways to improve your systems. This includes:
- Regular Maintenance
- Troubleshooting IT Problems
- Implementing IT Updates and Upgrades
Support Model
MSPs offer a blend of remote and onsite support. They provide regular reporting to keep you informed about your IT infrastructure’s status. Moreover, MSPs typically provide a user helpdesk for direct support.
II. Managed Security Service Providers (MSSP)
An MSSP, on the other hand, specializes in security services. Their primary focus is to protect your systems from various cyber threats.
Roles and Responsibilities of MSSPs
MSSPs offer specialized cybersecurity services:
- Firewall Management: They manage and monitor firewall systems to protect your network from threats.
- Intrusion Detection: They deploy intrusion detection systems to identify any malicious activity in your network.
- Incident Response and Management: They respond to and manage any security incidents to minimize damage.
- Vulnerability Testing: They conduct tests to identify and address any potential weaknesses in your network.
Proactive Approach to Cybersecurity
MSSPs, like MSPs, also take a proactive approach, but their focus is on maintaining your cybersecurity. This includes:
- Regular Security Audits
- Threat Intelligence and Analysis
- Implementation of Security Protocols and Updates
Compliance Management
MSSPs assist companies in meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring that data privacy and protection standards are met.
III. Key Differences between MSP and MSSP
While MSPs and MSSPs share some similarities, they have distinct differences:
- Focus: MSPs are centered on general IT services, whereas MSSPs specifically target security concerns.
- Nature of Services: MSPs offer operational support, while MSSPs provide security-focused services.
- Level of Expertise: MSSPs possess specialized knowledge and expertise in cybersecurity.
- Compliance Management: MSSPs specialize in ensuring compliance with regulations and data protection standards.
IV. Conclusion
Both MSPs and MSSPs play vital roles in today’s business landscape. MSPs maintain the operational efficiency of your IT systems, while MSSPs focus on safeguarding your digital assets from cyber threats. Depending on your business needs, you may require the services of one or both.
Understanding the differences and benefits of MSP vs MSSP empowers you to make informed decisions and strengthen your overall IT infrastructure and security.